Ensuring that your site is accessible will help to boost your SEO efforts, as it makes more of your content available to all users. Read our steps on how to improve your web accessibility and reap the rewards.
SEO and web accessibility have more in common than you may think. After all, the purpose of search engine optimisation is to help your target audience discover your brand and content effortlessly. The same can be said for website accessibility. At its core, accessibility ensures that the content on your website is discovered and perceived by literally anyone and when it comes to making the web accessible to people with disabilities, little steps can go a very long way. In this guide, we will focus on how web accessibility and SEO can work together to deliver a better user experience.
In this article, we will cover:
What is website accessibility?
How can web accessibility and SEO work together?
What is website accessibility?
Website accessibility refers to the practice of making websites and technologies accessible to users with physical and situational disabilities. The process aims to create a more inclusive web for people living with visual impairments, mobility restrictions, hearing impairments, seizures and cognitive disabilities. The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are the internationally recognised set of standards that are organised under four principles - Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust (POUR). Each guideline consists of testable success criteria that are not technology specific. This means that in order to meet the WCAG, the content on your website or app needs to meet the success criteria.
How can web accessibility and SEO work together?
There are many areas in which web accessibility and SEO overlap and by improving one, you can enhance the other. Here are six ways that can help both your accessibility and organic rankings:
1. Meta titles help screen headers and online rankings
A page title or a page tag is the name of a web page. It is found in the <title> tag in the page source and it’s the text found in the top of a user’s browser. Page titles also display in Google’s search result pages and are one of the first things people see when they search for a service or a product.

How do meta titles affect web accessibility?
People with disabilities will use screen readers to hear the page title. This is why it is important for the titles to be as descriptive and meaningful as possible. Creating logical page titles even for pages that may not seem important at first glance, such as the ‘About us’ or ‘Contact us’ pages, can bring value to customers who have visual impairments.
How do meta titles affect SEO?
Meta titles are important for organic rankings as they contain the main keyword the page is ranking for. Whilst Google has been rewriting meta titles in the SERPs, they have also confirmed that what you include in the meta title is still what search engines use to rank a webpage.
2. Breadcrumbs provide better UX
You will find breadcrumbs usually at the top of the page and indicate where the user is on the site. This is an example of the Mountain Warehouse website and whether a user lands on this category page organically, via Google or navigates to it from the Homepage, they will see this breadcrumb trail.

How do breadcrumbs help web accessibility?
According to the Success Criteria of the WCAG 2.1, breadcrumbs can help users with short attention span or people who become easily distracted or confused following a long navigation path.
How do breadcrumbs help SEO?
Breadcrumbs are great for SEO as they provide better user experience and additional internal links to the important pages on your site. There are different types of breadcrumbs, but hierarchy based breadcrumbs are the most common.
3. Headings help with content hierarchy
Headings help with on page user experience and also help search engine crawlers understand the structure of your page. There are 6 levels of headings (H1-H6), with H1 being the highest level heading on any given page. The different levels are important because they help communicate the structure and the hierarchy of the page.
How do headings affect web accessibility?
Headings allow users to quickly scan the content, which means they can navigate the page easily and find what they need quickly. Headings are also particularly useful for screen readers as they will communicate the different content on the page. Visually, headings are more prominent than the rest of the text which is especially helpful for people with cognitive disabilities or are easily distracted.
How do headings affect SEO?
Whilst the number of headings does not matter for SEO, we will advise you to always have one H1 heading and structure your content in a logical way. Google is known to use various headings on a page instead of meta titles so choose your headings wisely and incorporate the keywords you wish the article to appear for.
4. Alternative text on images provides context to both screen readers and search engines
Also referred to as alt text, alternative text is the description of the image and it is meant to convey what the image shows.
How does image alt text affect web accessibility?
The alt text is used by assistive technologies such as screen readers to help people who have visual impairment.
How does image alt text affect SEO?
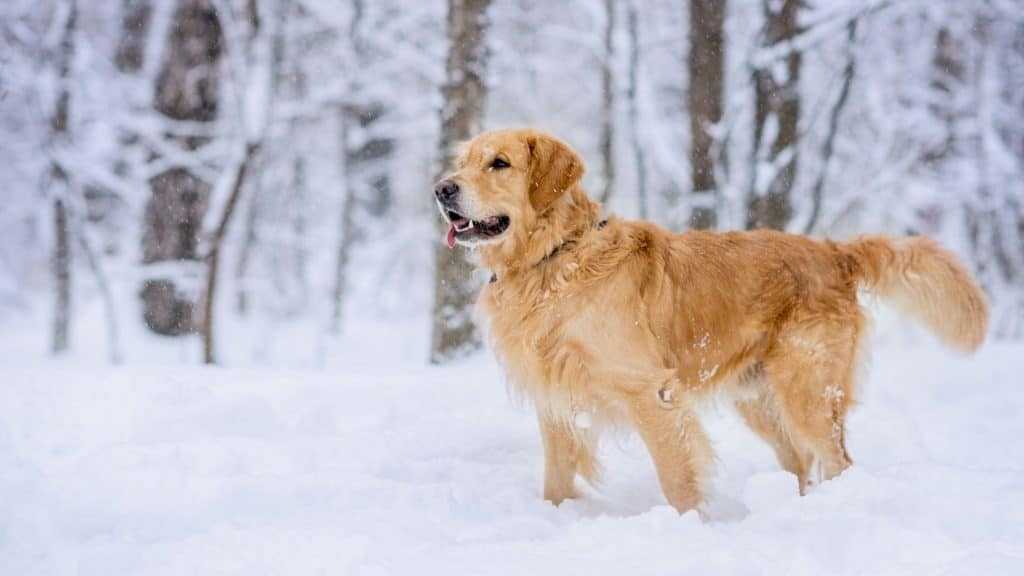
The alt text displays on the page if the image fails to load because of slow Internet connection or issues with the web server. Image alt text is also important for businesses using visuals to better communicate their products or services, e.g. e-commerce brands, interior designers, photographers, website designers, to name a few. To put this into context, this is an example of a good and bad image alt text.
Good: Golden retriever dog in the snow
Bad: Dog

5. Providing descriptive anchor text will give context to screen readers and search engines
Using descriptive links helps both web accessibility and SEO as they improve on page experience and topic relevance. Generic link text will include phrases such as: click this, click here, this, more, learn more. On the other hand, relevant anchor text examples include phrases such as: how to make a website more accessible, interactive content for SEO, or GA4 alternatives. The context provides relevance to both screen readers and search engine bots about the information found on the linked to page.
How does anchor text help web accessibility?
Screen readers can read a full page but they can also be set to read only the links on the page and so if the links are repetitive and lack context, the user will be confused. Additionally, different softwares may have issues with repetitive links.
How does anchor text help SEO?
Anchor text is important for both external and internal links as it adds context to the page and it tells readers what they will find on the other side of the link. Anchor text is not something that should be an afterthought and you should consider the location and the link text of both your internal and external links.
6. Mobile usability is ranking factor and provides better user experience
How does mobile usability affect web accessibility?
Good mobile experience puts the user first. Ensuring quick load times and that the text is legible, images are visible and the tap targets have enough space around them are just a few things you can review to ensure you are providing a good page experience.
How does mobile usability affect SEO?
Google has always placed importance on mobile performance, both from a ranking and user experience point of view. Mobile friendliness has been a confirmed ranking factor for a long time and Google predominantly uses the mobile version of your website to rank content (mobile-first indexing). This is why it’s important to ensure all of the content is visible on both desktop and mobile. You can also use Google’s Mobile Friendly tool to test your pages and see whether google bots are experiencing issues accessing any of your content.
Examples of businesses that have worked on web accessibility
- Twitter has allowed users to add alternative text to images since 2016, which provides advantages to people who require screen readers to access content. Twitter also confirmed that images containing alt text will display an ALT badge so that everybody can see the user generated image description.
- Just Eat Takeaway conducted research directly with people with disabilities in order to understand their experience better. This led them to improve their app by increasing tap targets. Tap targets are the space around a navigation button and as many of you probably know, they can be difficult to use on smaller screens. Tap targets are also really important for mobile usability, which is a ranking factor and it’s part of the Page Experience algorithm update. If you have problems with the tap targets on your website, this is usually something that Google will flag up in your Search Console Account.
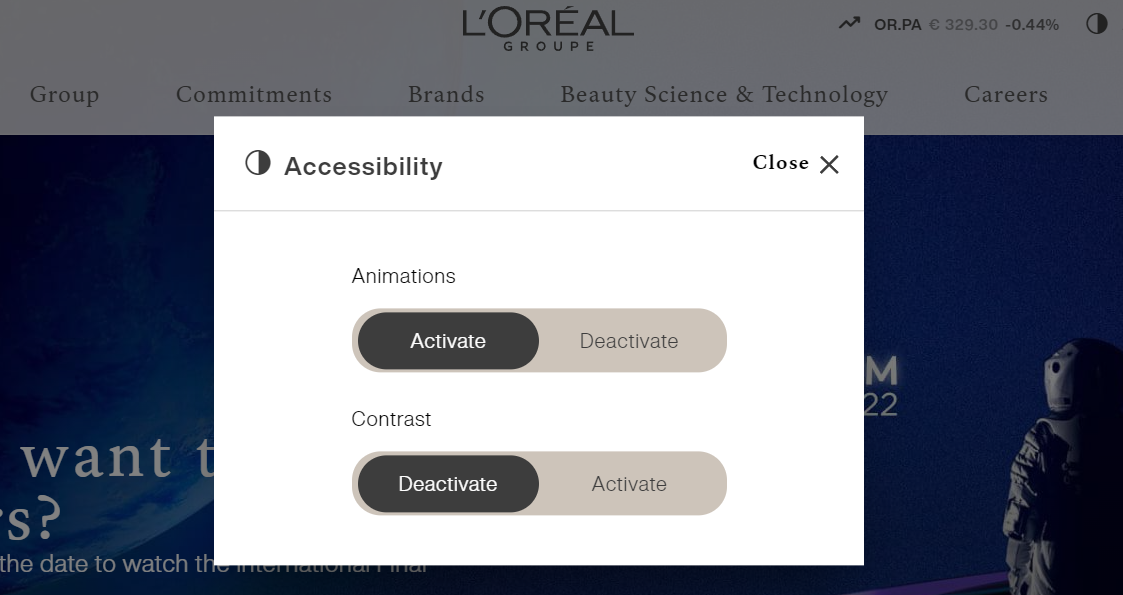
- L'Oréal built accessibility controls allowing users to activate or deactivate the animations and the contrast on the website. This makes it easier for readers to focus on the content and will help anyone who struggles with focus and attention.
- Booking.com discovered through testing that some of their navigational tabs are not working well with screen readers and partnered with experts to resolve this issue.
- Procter and Gamble introduced audio descriptions of their video ads and continue to make progress in this field.
How to become the accessibility champion in your company
Start by gaining an understanding of what web accessibility is and how it can impact users with physical disabilities. Audit your site by doing some manual checks (mobile performance, image alt text, meta titles and content structure) and use Google’s Lighthouse tool to see whether you are experiencing accessibility issues. Keep your team involved in the process and get them excited about providing a better user journey to people who live with physical disabilities. Next, make a plan of action and get a buy-in from the senior management team at your company. Work with people who will experience the issues first hand as well as web designers and SEOs who will ensure best practices are followed.
If you want to talk about SEO and web accessibility, you can reach me via Twitter @r_betelgeuse or connect with me on LinkedIn.




